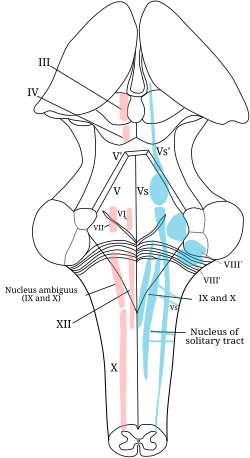Multiple cranial nerve nuclei are located on the floor of the fourth ventricle with a high risk of permanent damage.
Cranial nerve nuclei present in floor of 4th ventricle.
However the floor is the most related part to the cranial nerve nuclei.
B movement of these columns to the floor of the fourth ventricle in the embryonic rhombencephalon.
To identify patterns of cranial motor nuclei cmn displacement in cases of intramedullary brain stem tumor using neurophysiological mapping of motor nuclei on the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Where is the nuclei for the third cranial nerve the oculomotor.
The only naturally occurring openings between the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain are the foramina of luschka and magendie in the fourth ventricle.
The caudal tip of the fourth ventricle where it becomes the central canal is known as the obex.
10 3 is formed by the pons and medulla fig.
The floor of the fourth ventricle the rhomboid fossa see fig.
The fourth ventricle has a roof at its upper posterior surface and a floor at its lower anterior surface and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side.
Which two arteries does the oculomotor nerve lie between.
The obex is also a.
A arrangement of the general afferent and efferent cell columns in the embryonic spinal cord.
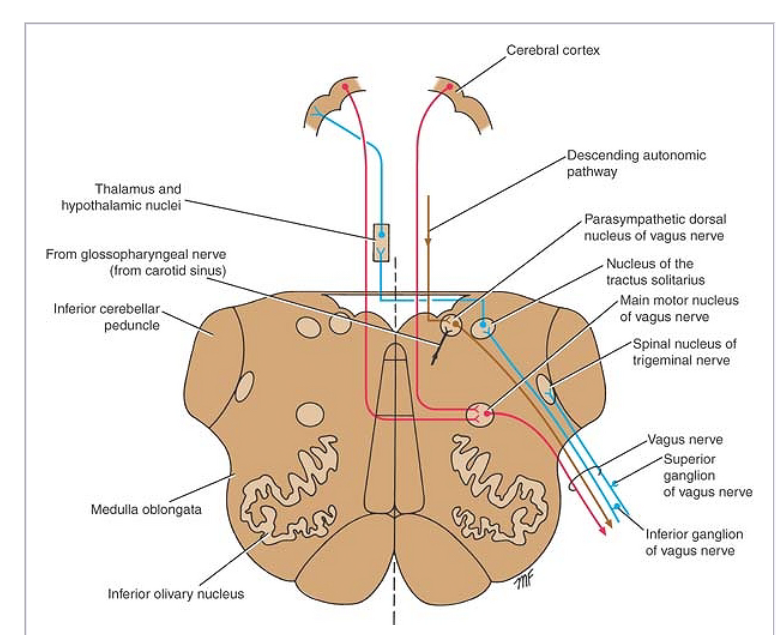
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons gray matter in the brain stem that is associated with one or more cranial nerves.
We present two cases illustrating the benefit of utilizing intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring ionm for prevention of injuries to the lower cranial nerves during fourth ventricle tumor resection surgeries.
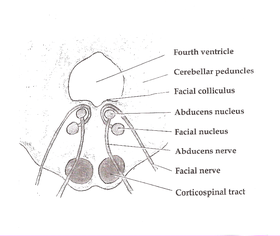
Floor of the fourth ventricle below the facial colliculus facial nerve passes above it at the pons.
The floor of the fourth ventricle often called the rhomboid fossa because of its shape is divisible into an upper triangular part formed by the posterior surface of the pons.
Surgical treatment of brainstem lesions carries a substantial risk of postoperative morbidity because of the risk of injuring the tightly packed cranial nerve nuclei cnn and neural tracts within the rhomboid fossa and brainstem lang et al 1991 historically neurosurgeons considered this area to be a no man s land with most lesions being inoperable baker 1965.
Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve s they are associated with.
A lower triangular part formed by the upper part of the posterior surface of the medulla.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13974/Cranial_nerve_nuclei.png)